golang网络通信超时设置方式
网络通信中,为了防止长时间无响应的情况,经常会用到网络连接超时、读写超时的设置。
本文结合例子简介golang的连接超时和读写超时设置。
1.超时设置1.1 连接超时
func DialTimeout(network, address string, timeout time.Duration) (Conn, error)
第三个参数timeout可以用来设置连接超时设置。
如果超过timeout的指定的时间,连接没有完成,会返回超时错误。
1.2 读写超时
在Conn定义中,包括读写的超时时间设置。
type Conn interface { // SetDeadline sets the read and write deadlines associated // with the connection. It is equivalent to calling both // SetReadDeadline and SetWriteDeadline. // ... ... SetDeadline(t time.Time) error // SetReadDeadline sets the deadline for future Read calls // and any currently-blocked Read call. // A zero value for t means Read will not time out. SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error // SetWriteDeadline sets the deadline for future Write calls // and any currently-blocked Write call. // Even if write times out, it may return n > 0, indicating that // some of the data was successfully written. // A zero value for t means Write will not time out. SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error}
通过上面的函数说明,可以得知,这里的参数t是一个未来的时间点,所以每次读或写之前,都要调用SetXXX重新设置超时时间,
如果只设置一次,就会出现总是超时的问题。
2.例子2.1 server
server端监听连接,如果收到连接请求,就是创建一个goroutine负责这个连接的数据收发。
为了测试超时,我们在写操作之前,sleep 3s。
package mainimport ( 'net' 'log' 'time')func main() { addr := '0.0.0.0:8080' tcpAddr, err := net.ResolveTCPAddr('tcp',addr) if err != nil { log.Fatalf('net.ResovleTCPAddr fail:%s', addr) } listener, err := net.ListenTCP('tcp', tcpAddr) if err != nil { log.Fatalf('listen %s fail: %s', addr, err) } else { log.Println('listening', addr) } for { conn, err := listener.Accept() if err != nil { log.Println('listener.Accept error:', err) continue } go handleConnection(conn) }}func handleConnection(conn net.Conn) { defer conn.Close() var buffer []byte = []byte('You are welcome. I’m server.') for { time.Sleep(3*time.Second)// sleep 3s n, err := conn.Write(buffer) if err != nil { log.Println('Write error:', err) break } log.Println('send:', n) } log.Println('connetion end')}
2.2 client
client建立连接时,使用的超时时间是3s。
创建连接成功后,设置连接的读超时。
每次读之前,都重新设置超时时间。
package mainimport ( 'log' 'net' 'os' 'time')func main() { connTimeout := 3*time.Second conn, err := net.DialTimeout('tcp', '127.0.0.1:8080', connTimeout) // 3s timeout if err != nil { log.Println('dial failed:', err) os.Exit(1) } defer conn.Close() readTimeout := 2*time.Second buffer := make([]byte, 512) for { err = conn.SetReadDeadline(time.Now().Add(readTimeout)) // timeout if err != nil { log.Println('setReadDeadline failed:', err) } n, err := conn.Read(buffer) if err != nil { log.Println('Read failed:', err) //break } log.Println('count:', n, 'msg:', string(buffer)) } }
输出结果
2019/05/12 16:18:19 Read failed: read tcp 127.0.0.1:51718->127.0.0.1:8080: i/o timeout2019/05/12 16:18:19 count: 0 msg:2019/05/12 16:18:20 count: 28 msg: You are welcome. I’m server.2019/05/12 16:18:22 Read failed: read tcp 127.0.0.1:51718->127.0.0.1:8080: i/o timeout2019/05/12 16:18:22 count: 0 msg: You are welcome. I’m server.2019/05/12 16:18:23 count: 28 msg: You are welcome. I’m server.2019/05/12 16:18:25 Read failed: read tcp 127.0.0.1:51718->127.0.0.1:8080: i/o timeout2019/05/12 16:18:25 count: 0 msg: You are welcome. I’m server.2019/05/12 16:18:26 count: 28 msg: You are welcome. I’m server.
补充:Golang中的并发限制与超时控制
并发
package mainimport ( 'fmt' 'time')func run(task_id, sleeptime int, ch chan string) { time.Sleep(time.Duration(sleeptime) * time.Second) ch <- fmt.Sprintf('task id %d , sleep %d second', task_id, sleeptime) return}func main() { input := []int{3, 2, 1} ch := make(chan string) startTime := time.Now() fmt.Println('Multirun start') for i, sleeptime := range input { go run(i, sleeptime, ch) } for range input { fmt.Println(<-ch) } endTime := time.Now() fmt.Printf('Multissh finished. Process time %s. Number of tasks is %d', endTime.Sub(startTime), len(input))}
函数 run() 接受输入的参数,sleep 若干秒。然后通过 go 关键字并发执行,通过 channel 返回结果。
channel 顾名思义,他就是 goroutine 之间通信的“管道'。管道中的数据流通,实际上是 goroutine 之间的一种内存共享。我们通过他可以在 goroutine 之间交互数据。
ch <- xxx // 向 channel 写入数据
<- ch // 从 channel 中读取数据
channel 分为无缓冲(unbuffered)和缓冲(buffered)两种。例如刚才我们通过如下方式创建了一个无缓冲的 channel。
ch := make(chan string)
channel 的缓冲,我们一会再说,先看看刚才看看执行的结果。
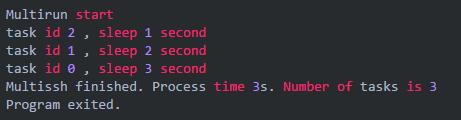
三个 goroutine `分别 sleep 了 3,2,1秒。但总耗时只有 3 秒。所以并发生效了,go 的并发就是这么简单。
按序返回
刚才的示例中,我执行任务的顺序是 0,1,2。但是从 channel 中返回的顺序却是 2,1,0。这很好理解,因为 task 2 执行的最快嘛,所以先返回了进入了 channel,task 1 次之,task 0 最慢。
如果我们希望按照任务执行的顺序依次返回数据呢?可以通过一个 channel 数组(好吧,应该叫切片)来做,比如这样
package mainimport ( 'fmt' 'time')func run(task_id, sleeptime int, ch chan string) { time.Sleep(time.Duration(sleeptime) * time.Second) ch <- fmt.Sprintf('task id %d , sleep %d second', task_id, sleeptime) return}func main() { input := []int{3, 2, 1} chs := make([]chan string, len(input)) startTime := time.Now() fmt.Println('Multirun start') for i, sleeptime := range input { chs[i] = make(chan string) go run(i, sleeptime, chs[i]) } for _, ch := range chs { fmt.Println(<-ch) } endTime := time.Now() fmt.Printf('Multissh finished. Process time %s. Number of tasks is %d', endTime.Sub(startTime), len(input))}
超时控制
刚才的例子里我们没有考虑超时。然而如果某个 goroutine 运行时间太长了,那很肯定会拖累主 goroutine 被阻塞住,整个程序就挂起在那儿了。因此我们需要有超时的控制。
通常我们可以通过select + time.After 来进行超时检查,例如这样,我们增加一个函数 Run() ,在 Run() 中执行 go run() 。并通过 select + time.After 进行超时判断。
package mainimport ( 'fmt' 'time')func Run(task_id, sleeptime, timeout int, ch chan string) { ch_run := make(chan string) go run(task_id, sleeptime, ch_run) select { case re := <-ch_run: ch <- re case <-time.After(time.Duration(timeout) * time.Second): re := fmt.Sprintf('task id %d , timeout', task_id) ch <- re }}func run(task_id, sleeptime int, ch chan string) { time.Sleep(time.Duration(sleeptime) * time.Second) ch <- fmt.Sprintf('task id %d , sleep %d second', task_id, sleeptime) return}func main() { input := []int{3, 2, 1} timeout := 2 chs := make([]chan string, len(input)) startTime := time.Now() fmt.Println('Multirun start') for i, sleeptime := range input { chs[i] = make(chan string) go Run(i, sleeptime, timeout, chs[i]) } for _, ch := range chs { fmt.Println(<-ch) } endTime := time.Now() fmt.Printf('Multissh finished. Process time %s. Number of task is %d', endTime.Sub(startTime), len(input))}
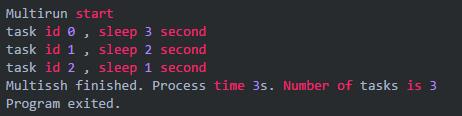
运行结果,task 0 和 task 1 已然超时
并发限制
如果任务数量太多,不加以限制的并发开启 goroutine 的话,可能会过多的占用资源,服务器可能会爆炸。所以实际环境中并发限制也是一定要做的。
一种常见的做法就是利用 channel 的缓冲机制。我们分别创建一个带缓冲和不带缓冲的 channel 看看
ch := make(chan string) // 这是一个无缓冲的 channel,或者说缓冲区长度是 0
ch := make(chan string, 1) // 这是一个带缓冲的 channel, 缓冲区长度是 1
这两者的区别在于,如果 channel 没有缓冲,或者缓冲区满了。goroutine 会自动阻塞,直到 channel 里的数据被读走为止。举个例子
package mainimport ( 'fmt')func main() { ch := make(chan string) ch <- '123' fmt.Println(<-ch)}
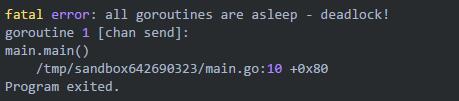
这段代码执行将报错
fatal error: all goroutines are asleep - deadlock!goroutine 1 [chan send]:main.main() /tmp/sandbox531498664/main.go:9 +0x60Program exited.
这是因为我们创建的 ch 是一个无缓冲的 channel。因此在执行到 ch<-'123',这个 goroutine 就阻塞了,后面的 fmt.Println(<-ch) 没有办法得到执行。所以将会报 deadlock 错误。
如果我们改成这样,程序就可执行
package mainimport ( 'fmt')func main() { ch := make(chan string, 1) ch <- '123' fmt.Println(<-ch)}
执行
123
Program exited.
如果我们改成这样
package mainimport ( 'fmt')func main() { ch := make(chan string, 1) ch <- '123' ch <- '123' fmt.Println(<-ch) fmt.Println(<-ch)}
尽管读取了两次 channel,但是程序还是会死锁,因为缓冲区满了,goroutine 阻塞挂起。第二个 ch<- '123' 是没有办法写入的。
因此,利用 channel 的缓冲设定,我们就可以来实现并发的限制。我们只要在执行并发的同时,往一个带有缓冲的 channel 里写入点东西(随便写啥,内容不重要)。让并发的 goroutine 在执行完成后把这个 channel 里的东西给读走。这样整个并发的数量就讲控制在这个 channel 的缓冲区大小上。
比如我们可以用一个 bool 类型的带缓冲 channel 作为并发限制的计数器。

然后在并发执行的地方,每创建一个新的 goroutine,都往 chLimit 里塞个东西。
for i, sleeptime := range input { chs[i] = make(chan string, 1) chLimit <- true go limitFunc(chLimit, chs[i], i, sleeptime, timeout)}
这里通过 go 关键字并发执行的是新构造的函数。他在执行完原来的 Run() 后,会把 chLimit 的缓冲区里给消费掉一个。
limitFunc := func(chLimit chan bool, ch chan string, task_id, sleeptime, timeout int) { Run(task_id, sleeptime, timeout, ch) <-chLimit}
这样一来,当创建的 goroutine 数量到达 chLimit 的缓冲区上限后。主 goroutine 就挂起阻塞了,直到这些 goroutine 执行完毕,消费掉了 chLimit 缓冲区中的数据,程序才会继续创建新的 goroutine。我们并发数量限制的目的也就达到了。
完整示例代码
package mainimport ( 'fmt' 'time')func Run(task_id, sleeptime, timeout int, ch chan string) { ch_run := make(chan string) go run(task_id, sleeptime, ch_run) select { case re := <-ch_run: ch <- re case <-time.After(time.Duration(timeout) * time.Second): re := fmt.Sprintf('task id %d , timeout', task_id) ch <- re }}func run(task_id, sleeptime int, ch chan string) { time.Sleep(time.Duration(sleeptime) * time.Second) ch <- fmt.Sprintf('task id %d , sleep %d second', task_id, sleeptime) return}func main() { input := []int{3, 2, 1} timeout := 2 chLimit := make(chan bool, 1) chs := make([]chan string, len(input)) limitFunc := func(chLimit chan bool, ch chan string, task_id, sleeptime, timeout int) { Run(task_id, sleeptime, timeout, ch) <-chLimit } startTime := time.Now() fmt.Println('Multirun start') for i, sleeptime := range input { chs[i] = make(chan string, 1) chLimit <- true go limitFunc(chLimit, chs[i], i, sleeptime, timeout) } for _, ch := range chs { fmt.Println(<-ch) } endTime := time.Now() fmt.Printf('Multissh finished. Process time %s. Number of task is %d', endTime.Sub(startTime), len(input))}
运行结果
Multirun starttask id 0 , timeouttask id 1 , timeouttask id 2 , sleep 1 secondMultissh finished. Process time 5s. Number of task is 3Program exited.
chLimit 的缓冲是 1。task 0 和 task 1 耗时 2 秒超时。task 2 耗时 1 秒。总耗时 5 秒。并发限制生效了。
如果我们修改并发限制为 2
chLimit := make(chan bool, 2)
运行结果
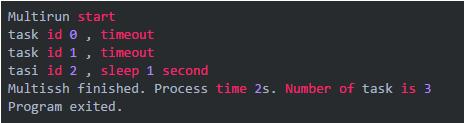
Multirun starttask id 0 , timeouttask id 1 , timeouttask id 2 , sleep 1 secondMultissh finished. Process time 3s. Number of task is 3Program exited.
task 0 , task 1 并发执行,耗时 2秒。task 2 耗时 1秒。总耗时 3 秒。符合预期。
有没有注意到代码里有个地方和之前不同。这里,用了一个带缓冲的 channel
chs[i] = make(chan string, 1)
还记得上面的例子么。如果 channel 不带缓冲,那么直到他被消费掉之前,这个 goroutine 都会被阻塞挂起。
然而如果这里的并发限制,也就是 chLimit 生效阻塞了主 goroutine,那么后面消费这些数据的代码并不会执行到。。。于是就 deadlock 拉!
for _, ch := range chs { fmt.Println(<-ch)}
所以给他一个缓冲就好了。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持优爱好网。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
相关文章:
1. Flutter刷新组件RefreshIndicator自定义样式demo2. requestAnimationFrame使用示例详解3. 基于JavaScript实现图片裁剪功能4. 怎么让div+css兼容ie6ie7ie8ie9和FireFoxChrome等浏览器5. uniapp自定义验证码输入框并隐藏光标6. 详解JavaScript中原始数据类型Symbol的使用7. JavaScript深拷贝方法structuredClone使用8. uniapp 手机验证码输入框实现代码(随机数、倒计时、隐藏手机号码中间四位)可以直接使用9. 使用Node.js实现Clean Architecture方法示例详解10. js的一些潜在规则使用分析
- 排行榜

- IE和firefox浏览器的event事件兼容性怎么样?兼容性详情说明
- 1. Golang单元测试与覆盖率的实例讲解
- 2. 浅谈Golang 嵌套 interface 的赋值问题
- 3. IE浏览器在post提交时中文乱码是什么原因?解决乱码的方法说明
- 4. xml中的空格之完全解说
- 5. 模拟OICQ的实现思路和核心程序(一)
- 6. 程序员视频以及文档教程
- 7. 解决golang在import自己的包报错的问题
- 8. IE浏览器专有css属性之zoom?具体详情介绍
- 9. IE浏览器的haslayout属性和相关兼容性问题怎么解决?解决方法分享
- 10. Electron调用外接摄像头并拍照上传实现详解
 网公网安备
网公网安备