基于MySQL和Redis扣减库存的实践
目录
- 背景
- 环境搭建
- 后台系统
- 中间件
- 测试工具
- 扣减模式
- 基于数据库行锁 + CAS 实现库存的扣减
- 基于 Redis 实现库存的扣减
- 总结
背景
在很多情况下,扣减库存是一个十分常见的需求,例如:学生选课系统中课程数量的扣减,抽奖系统中活动次数的扣减,电商系统中商品库存的扣减等,都涉及到数量的扣减,这些系统在成功扣减的前提下,绝对不能出现库存扣减多了的情况,也就是不能出现超卖。同时,我们也要注重系统性能的提升,这篇文章从这两个角度进行分析和讨论。
环境搭建
后台系统
基于 SpringBoot 搭建后台系统,JDK 为 1.8
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<spring-boot.version>2.3.12.RELEASE</spring-boot.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
中间件
中间件使用 MySQL + Redis 进行数据的存储,使用 Mybatis 作为 ORM 框架
create database t_desc collate utf8mb4_general_ci;
use t_desc;
create table t_good (
id bigint auto_increment primary key comment '自增id',
good_name varchar(255) not null comment '商品名称',
stock int not null comment '商品库存'
) comment '库存测试表';
insert into t_good(good_name, stock) value('iphone', 50);
创建一张商品库存表,里面含有商品 id、商品名称 和库存 3 个字段,所有扣减库存的操作都在这张表上进行;
测试工具
使用 JMeter 5.5 进行测试
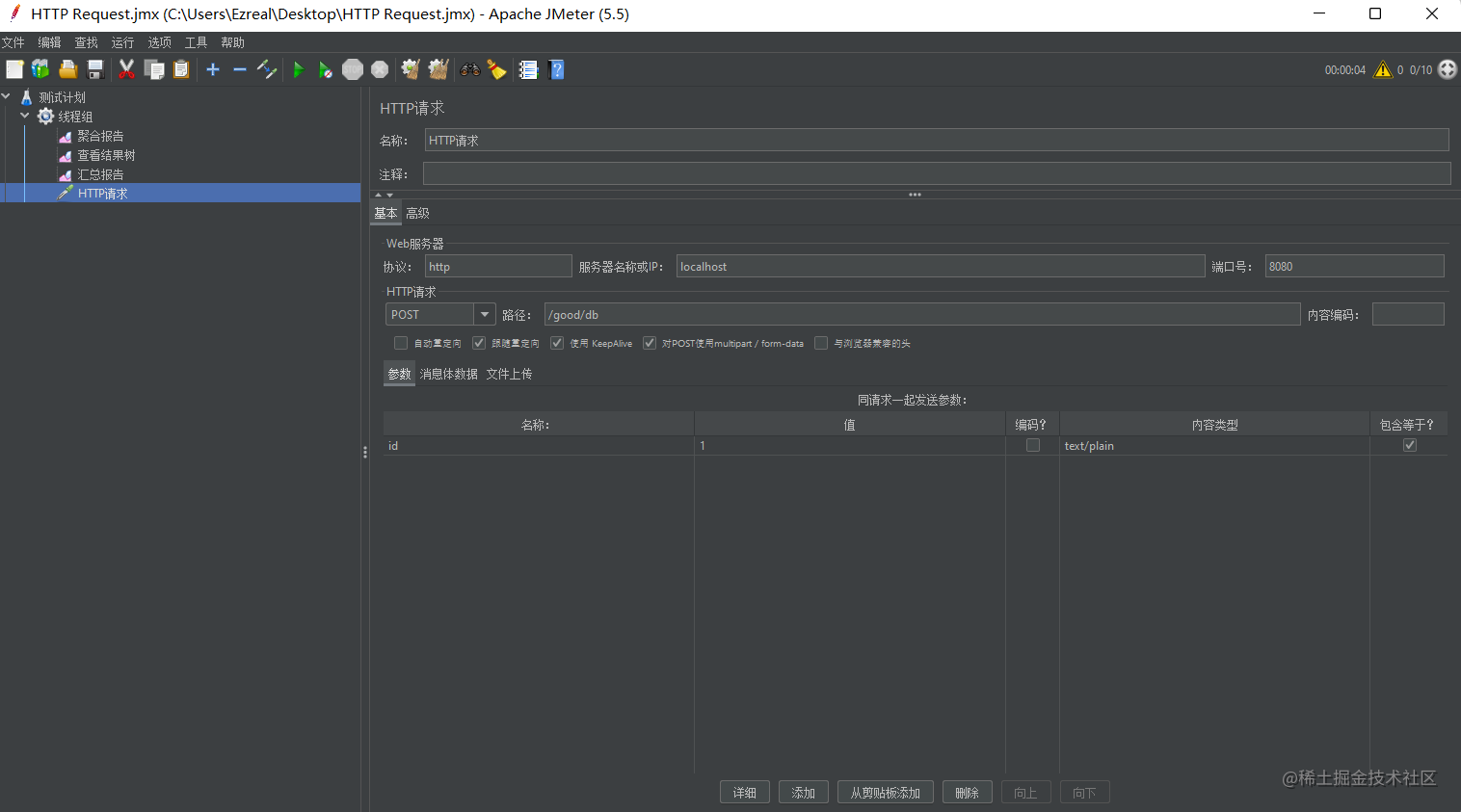
以下的库存数量统一设置为 50 个,线程组的数量为 10 个,循环 10 次,共 100 个扣减请求,最终正确的结果应该是扣减完毕后库存的数量应该为 0, 而不是 -50
扣减模式
基于数据库行锁 + CAS 实现库存的扣减
行锁
若直接直接在数据库层面进行库存的直接扣减,100 个线程同时进行请求,肯定会造成库存的超卖
SQL 语句为
<update id="descGoodStock">
update t_desc.t_good
set t_good.stock = t_good.stock - 1
where id = #{id}
</update>
考虑到 update 语句,若根据主键索引作为条件进行更新,会对数据库的某一行加上行锁(数据库开启事务自动提交),所以我们加上 stock > 0 的判断条件
<update id="descGoodStockByLock">
update t_desc.t_good
set t_good.stock = t_good.stock - 1
where id = #{id}
and t_good.stock > 0
</update>
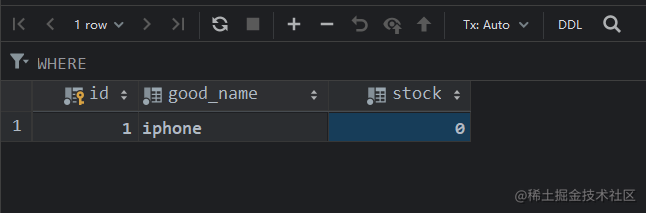
开启 JMeter 进行测试,可见没有超卖
CAS
CAS 即 Compare and Set,先把旧的库存查出来,再把旧的库存作为 update 的条件之一,若数据库中的库存与旧的库存一致,则进行更新,否则不进行更新。
其实本质上与行锁的方式没什么区别,而且多了一次查询,写这个方法只是为了记录而已
若有两个以上的线程先查询到了商品的旧库存,这种方法可能会出现扣不完的情况
Java 代码:
@PostMapping("/db")
public Map<String, Object> goodDescControllerByDataBase(Long id) {
HashMap<String, Object> ret = new HashMap<>();
// 查出旧的值
Good good = goodMapper.selectStockById(id);
// 再进行更新
int i = goodMapper.descGoodStockCAS(id, good.getStock());
if (i > 1) {
ret.put("info", "success, 扣减成功");
} else {
ret.put("info", "fail, 扣减失败");
}
return ret;
}
SQL 语句
<update id="descGoodStockCAS">
update t_desc.t_good
set t_good.stock = t_good.stock - 1
where id = #{id}
and t_good.stock = #{stock}
and t_good.stock > 0
</update>
测试结果:
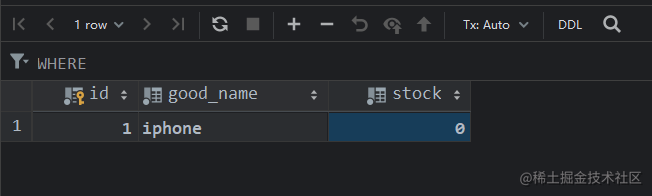
综上,基于数据库的两种扣减库存的方式都没有实现超卖,但是毕竟是数据库,数据存储于物理磁盘中,性能方面就有待考量;
基于 Redis 实现库存的扣减
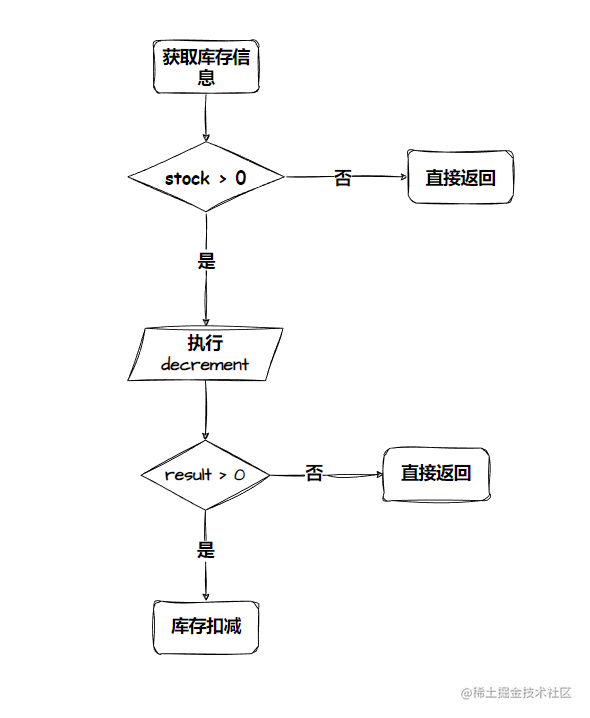
基本思想是:我们把库存的数量提前放到 Redis 上,直接在 Redis 进行库存的扣减
- 先查询 redis 中的库存
- 若小于 0 直接返回
- 若大于 0 则进行 Redis 和 数据库 中的库存扣减
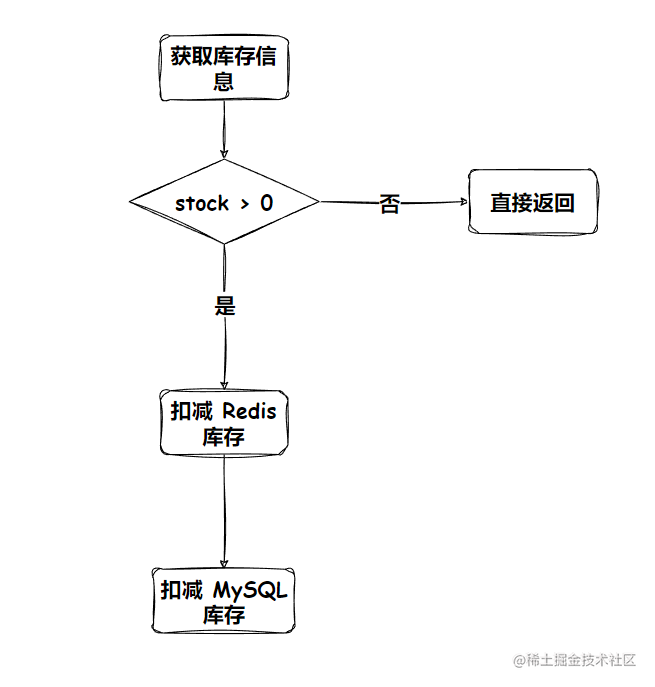
不过这里存在 并发 问题,考虑极限情况,两个线程同时获得 stock = 1,然后再去进行库存扣减,势必会造成超卖的现象
下面给出两种解决办法
使用 decrement 方法
redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement():对某个 key 进行减 1 操作,会返回扣减后的值
若该值大于等于 0 才进行数据库的库存的扣减,否则直接返回库存不足的提示
这种方法是基于 Redis 的指令是原子性的
Java 代码:
@PostMapping("/redis")
public Map<String, Object> goodDescControllerByRedis(Long id) throws InterruptedException {
HashMap<String, Object> ret = new HashMap<>();
ret.put("info", "fail, 扣减失败");
// 查询 Redis 中的库存
Integer stock = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key + id);
Thread.sleep(100);
if (stock <= 0) {
return ret;
}
// 扣减 redis 中库存
Long decrement = redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement(key + id);
if (decrement >= 0) {
// 扣减数据库库存
goodMapper.descGoodStock(id);
ret.put("info", "success, 扣减成功");
}
return ret;
}
其实 decrement 方法是原子性的,可以不用对库存先进行查询的操作,只需要判断扣减后的数是否大于 0 即可。但是如果并发量高的话,建议还是加上判断的逻辑,可以提高 Redis 的性能,不用每次进行 decrement 操作;
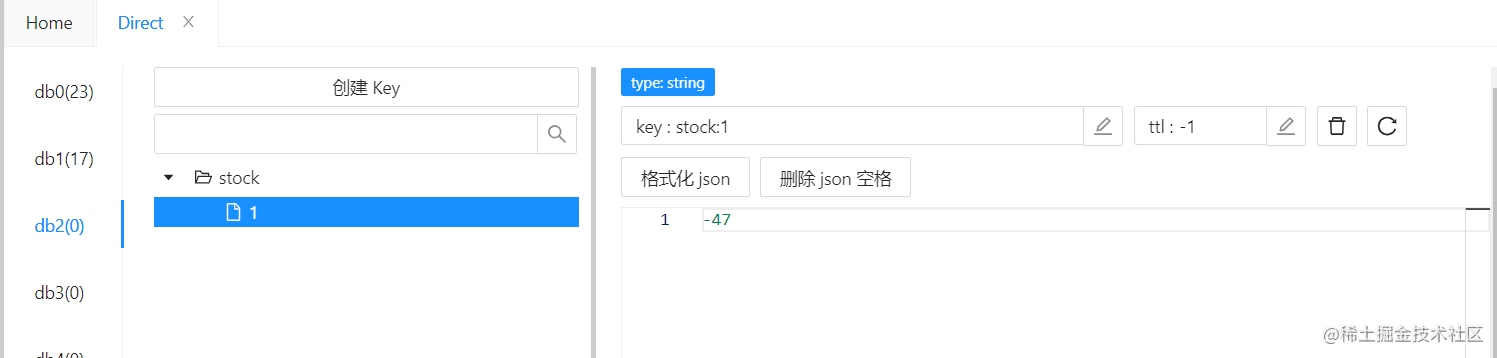
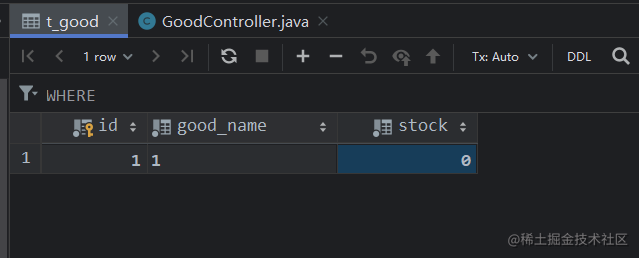
缺点:这种办法会导致 Redis 中库存产生超卖现象,若对 Redis 中库存数量要求准确,就不要使用这种方法;
测试结果:
Redis 中的库存产生超卖现象:
MySQL 中的库存没有超卖:
使用 LUA 脚本
上述问题的关键是:查询 和 扣减 是两个分开操作,不是一条原子性的命令。我们可以使用 LUA 脚本,把这两条命令封装到 LUA 代码中,实现这两个操作的原子性
LUA 代码
---
--- Generated by EmmyLua(https://github.com/EmmyLua)
--- Created by Ezreal.
--- DateTime: 2023/5/6 21:56
---
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 1) then
local stock = tonumber(redis.call('get', KEYS[1]));
if (stock <= 0) then
return -1;
end
if (stock > 0) then
redis.call('incrby', KEYS[1], -1);
return 1;
end
end
return -1
先获取值,然后判断库存数量,若没有小于等于 0 就先进行扣减即可
Java 代码
private static final DefaultRedisScript<Long> DECREASE_GOOD_STOCK_SCRIPT = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
static {
DECREASE_GOOD_STOCK_SCRIPT.setLocation(new ClassPathResource("/lua/desc_stock.lua"));
// 设置返回值类型
DECREASE_GOOD_STOCK_SCRIPT.setResultType(Long.class);
}
@PostMapping("/lua")
public Map<String, Object> goodDescControllerByLUA(Long id) {
List<String> keys = new ArrayList<>();
keys.add("stock:" + id);
HashMap<String, Object> ret = new HashMap<>();
ret.put("info", "fail, 扣减失败");
Long execute = redisTemplate.execute(DECREASE_GOOD_STOCK_SCRIPT, keys);
if (execute == 1) {
goodMapper.descGoodStock(id);
ret.put("info", "success, 扣减成功");
}
return ret;
}
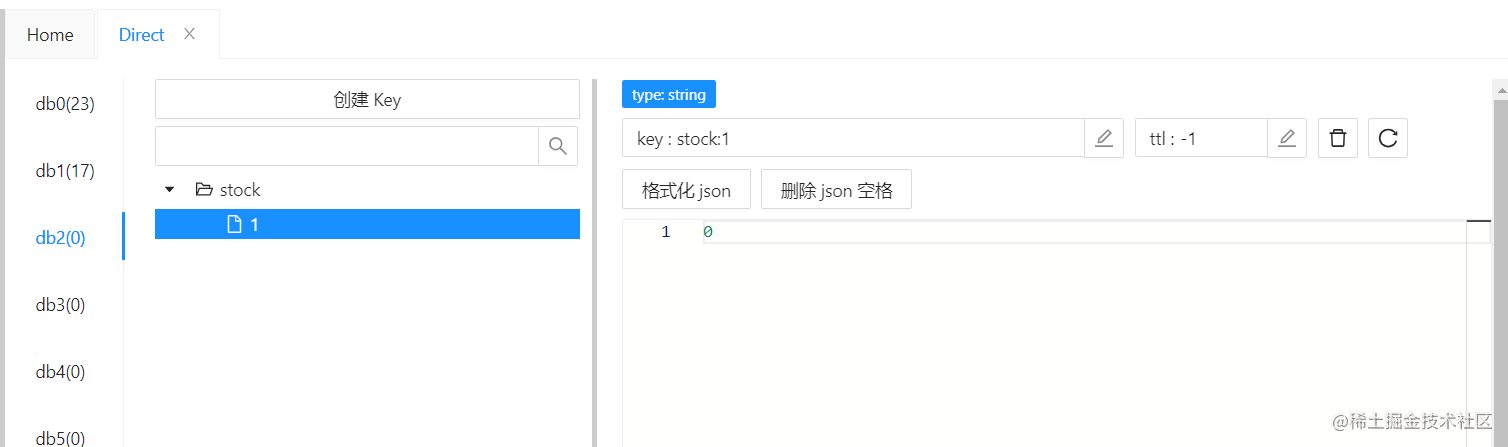
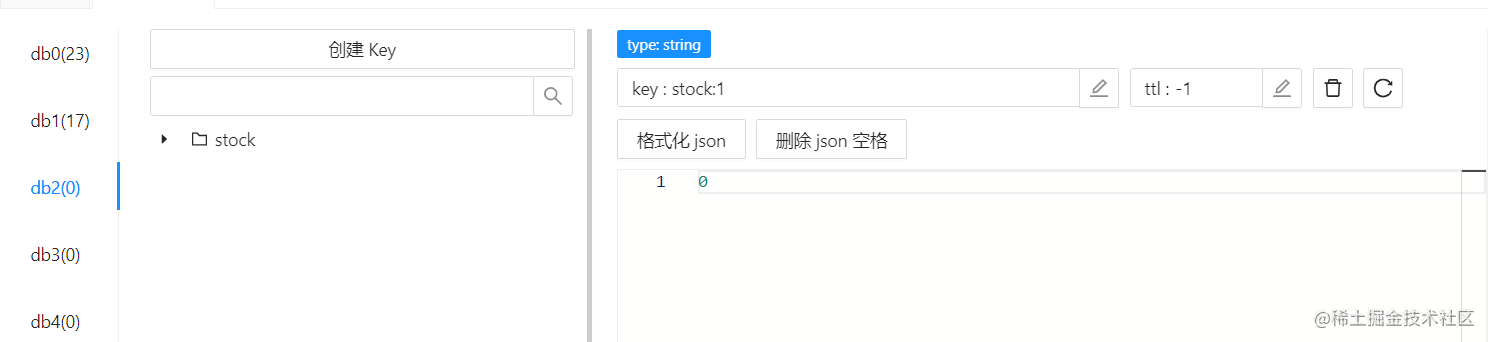
结果:Redis 和 MySQL 中的库存均为 0 ,没有超卖
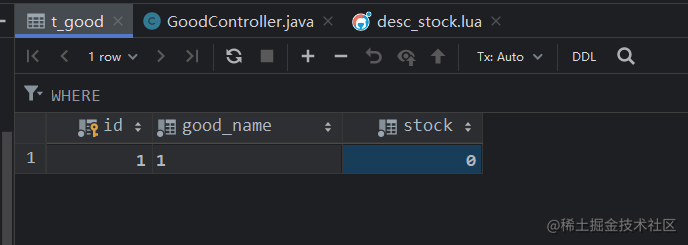
使用分布式锁
可以使用 redisson 分布式锁进行扣减库存处理,锁住查询和扣减两个步骤即可;
若是在分布式环境下,要考虑 分布式锁 与 LUA 脚本的结合!
java 代码
@PostMapping("/lock")
public Map<String, Object> goodDescControllerByLock(Long id) throws InterruptedException {
HashMap<String, Object> ret = new HashMap<>();
ret.put("info", "fail, 扣减失败");
// 加锁
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("stock" + id);
boolean tryLock = lock.tryLock(2L, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (tryLock) {
Integer stock = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key + id);
if (stock <= 0) {
return ret;
}
Long decrement = redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement(key + id);
if (decrement >= 0) {
goodMapper.descGoodStock(id);
ret.put("info", "success, 扣减成功");
}
}
return ret;
}
测试结果:
Redis 中库存数量没有超卖
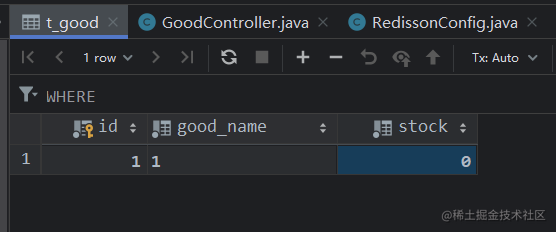
MySQL 中库存数量没有超卖
总结
如果在项目初期流量较少可以考虑基于 数据库行锁 进行库存的扣减,到了后期流量大,几乎都要用到 Redis:
- decrement:追求简单快速实现,不考虑 Redis 库存中的准确性;
- LUA 脚本:追求 Redis 中库存的准确性,在 Redis 层面上要进行多重的条件判断
- Lock:追求 Redis 中库存的准确性,在分布式环境中要考虑 LUA + Lock 的结合
到此这篇关于基于MySQL和Redis扣减库存的实践的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关MySQL和Redis扣减库存内容请搜索以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持!
 网公网安备
网公网安备